Prehistoric Eras
Exploring Historical Periods and Prehistoric Eras
Introduction
Welcome to a journey through time as we delve into the fascinating world of historical periods and prehistoric eras. From the ancient civilizations to the dawn of humankind, each era has its unique characteristics and developments that have shaped the world we live in today.
Prehistoric Era
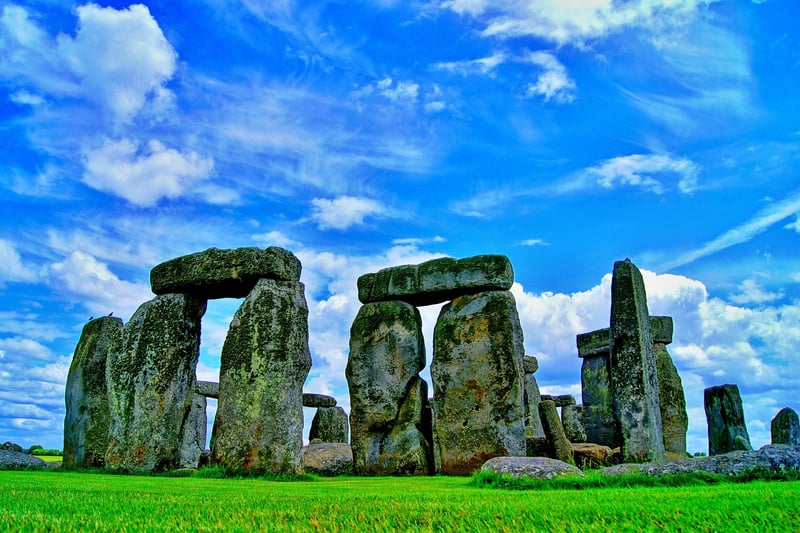
The Prehistoric Era refers to the time before written records existed. It is divided into three main periods:
- Paleolithic Age: Also known as the Old Stone Age, this period dates back to around 2.5 million years ago. It was characterized by the use of simple stone tools and the development of early human societies.
- Mesolithic Age: Following the Paleolithic Age, the Mesolithic Age marked a transitional period where humans began to settle in one place and develop more advanced tools and technologies.
- Neolithic Age: The Neolithic Age, or New Stone Age, witnessed the rise of agriculture, animal domestication, and the establishment of permanent settlements. This period laid the foundation for the development of complex societies.
Historical Periods
As we move into recorded history, several key historical periods emerge, each with its own significant events and cultural advancements:
Ancient Civilizations
The Ancient Civilizations period witnessed the rise of great empires such as the Egyptians, Greeks, Romans, and Mesopotamians. These civilizations made significant contributions to art, architecture, philosophy, and governance.
Medieval Era
The Medieval Era spanned from the 5th to the 15th century and was characterized by feudalism, the rise of Christianity, and the establishment of powerful kingdoms and empires like the Byzantine Empire and the Holy Roman Empire.
Renaissance
The Renaissance, meaning "rebirth," was a period of cultural revival that took place in Europe from the 14th to the 17th century. It marked a resurgence in art, literature, science, and exploration, leading to significant advancements in various fields.
Industrial Revolution
The Industrial Revolution, which began in the late 18th century, transformed society with the introduction of mechanized manufacturing processes, steam power, and urbanization. It marked a shift from agrarian economies to industrialized nations.
Conclusion
Exploring historical periods and prehistoric eras allows us to gain valuable insights into the development of human civilization over time. By studying the achievements and challenges of our ancestors, we can better understand the world we inhabit today and appreciate the progress that has been made throughout history.